introduction
Introduction to Document Object Model
DOM is an interface to interact with the contents of a webpage. All elements in a webpage can be described in a Document Object Model (DOM). What this means is that every HTML or SVG document can be represented as a tree of objects. This object model is commonly used with JavaScript to create dynamic HTML. In a DOM, all the HTML elements of a webpage like tags, attributes, comments and content are divided into the units called Nodes.
A DOM consists of a document structure and a set of interfaces that allow you to perform operations on each node of the document
For example, tags are called element nodes and attributes of a tag are called attribute nodes, similarly text data are called text nodes and comments are called comments nodes and so on.
Look at the following code :
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My Heading</h1>
<p>Hello World!</p>
<p>This is DOM</p>
</body>
</html>
The DOM tree structure for this code would be something like this :
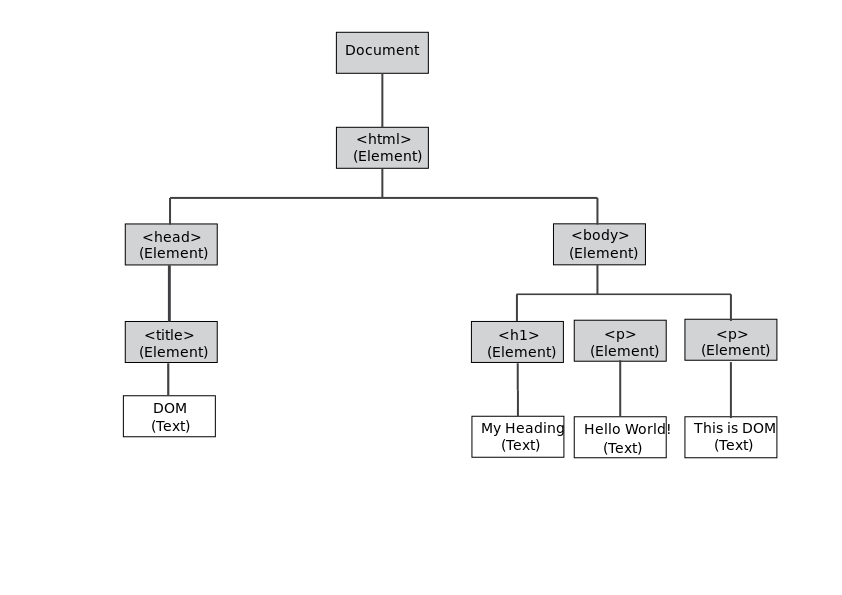
The DOM follows a hierarchical structure.
In the example, the body tag is the parent node of the h1 and p tags because they are described inside the body tag. Similarly the html tag is the parent node of the body tag.
The p tags and the h1 tags have a common parent in the body tag. When this happens the tags are called sibling nodes.
All the nodes located under a certain node are descendant nodes, and a node located on the top of the parent nodes is an ancestor node.