color
Summary
This page explains the different mechanisms available in HTML and CSS to specify colors.
Basic HTML Color keywords
The HTML 4.01 spec defines 16 color keywords. These colors can always be rendered properly, regardless of the color resolution of the user’s display card. As an example, you can specify pure red text in CSS with the following:
color: red; /* color rendered pure red */
The Cascading Style Sheets, Level 2 Revision 1 (CSS2.1) specification includes “orange” (#FFA500) for a total of 17 color keywords.
Extended Color keywords
In addition to the colors listed above, most browsers support an extended list of color keywords. The links below point to tables of colors sorted in various ways. The named colors do not represent the full color spectrum; therefore, for best results, use RGB or HSL color values. The basic and extended color keywords are defined in the CSS Color Module Level 3 Extended Color Keywords section.
Hexadecimal and RGB Notation
An RGB color value can be specified in two ways:
- A ‘#’ immediately, followed by a triad of two-digit hexadecimal numbers specifying the intensity of the three component color channels: red, green, and blue, respectively.
color: #FF0000; /* Text rendered pure red because the red channel is set to its highest value, FF.*/
There is also a shorthand notation that is three digits long instead of six, for example #FFF. This syntax is supported by all old and new browser however, different browser, operating platforms, and monitors, sometimes display color a little differently. The three digit hex color palette is shorter then the six digit color palette. So while the shorthand will save a few bytes in size there are less color options available as a result. Consider the example for the color pure red:
color: #FF0000; /* Six total, two hexadecimal digits in each of the three parts. */
color: #F00; /* Three total, one hexadecimal digits in each of the three parts. */
- The RGB() function, which contains three values delimited by commas specifying the intensity of the three component color channels: red, green, and blue, respectively. The above red color can be specified by either of the following:
color: rgb(255,0,0) /* text rendered pure red because the red channel is set to its highest integer value, 255.*/
color: rgb(100%,0%,0%) /* text rendered pure red because the red channel is set to its highest percentage value, 100%.*/
Why 255? modern computers use 256-bit color, which means they can display around 16.7 million different colors (256 x 256 x 256; hexadecimal numbers have 16 different values, 0-9 and then a-f — 16 x 16 = 255). And since computers count from 0, not 1, the value range is 0-255, not 1-256.
RGBA Notation
In modern browsers (Opera, Firefox, Chrome, Safari, and Internet Explorer 9+), a counterpart to the RGB color model is supported — RGBA — which can also accept an “alpha” value specifying the opacity of a color. The format of an RGBA value is the same as RGB, with the addition of a numerical value between 0 (completely transparent and therefore invisible) and 1 (completely opaque).
color: rgba(255,0,0,0.5) /* text rendered semi-transparent red */
color: rgba(100%,0%,0%,0.5) /* text rendered semi-transparent red */
HSL and HSLA notation
Modern browsers (Opera, Firefox, Chrome, Safari, and Internet Explorer 9+) also support an <acronym title="Hue Saturation Lightness">HSL</acronym> color model, which is also a function taking three values:
- The hue takes a degree value in the range of 0-360, representing how far round a standard colour wheel the color sits. The table below gives you an idea of how this works.
| Degree | Name | Color |
|---|---|---|
| 0° | red | |
| 60 | yellow | |
| 120 | lime | |
| 180 | cyan | |
| 240 | blue | |
| 300 | magenta | |
| 360 | red |
- Saturation is represented as a percentage, where
100%is full color saturation and0%percent is a shade of gray. - Lightness is also represented as a percentage, where
50%percent is normal,0%is pure black, and100%is pure white.
HSL also has a corresponding function that accepts an alpha channel value — HSLA hsla() alpha counterpart that allows you to specify opacity by using a numerical value between 1 and 0.
color: hsl(0, 100%, 50%) /* red */
color: hsla(0, 100%, 50%, 0.5) /* semi-transparent red */
color: hsl(120, 100%, 50%) /* lime green */
color: hsl(120, 100%, 20%) /* dark green */
color: hsl(120, 100%, 80%) /* light green */
color: hsl(120, 75%, 75%) /* pastel green */
System Colors
Note: CSS2 System Color values have been deprecated in favor of the CSS3 appearance property. If you want to emulate the look of a user interface related element or control, please use the ‘appearance’ property instead of attempting to mimic a user interface element through a combination of system colors.
It is also possible to specify system colors, so you can specify for example that you want your text to be the same color as your highlighted text; these are only supported on Windows. Unlike the named colors, system colors have no numeric RGB equivalent because the exact color is not known until the Web page is viewed on the user’s system. In this way, system colors are user-defined because users can choose their own system color scheme from the Windows Control Panel. The following table demonstrates appropriate text and background colors, as they would appear on a Windows Vista system with default colors.
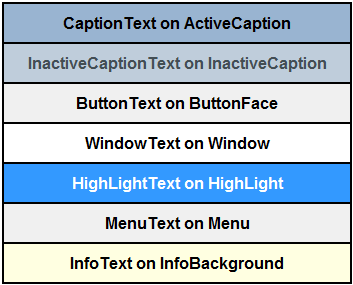
Note that the system color names have been deprecated in the http://www.w3.org/TR/css3-color/ CSS Color Module Level 3] recommendation, and since they are Windows-only, so it is advisable to not use them.
For a complete list of system colors, see User-Defined System Colors.
currentColor
- You can use the
currentColorvalue to set a color to the computed value of the element’scolorpropety. for example, the background color of the div in the following example will be red, the same color as thecolorof it’s parent element.
<article style="color:red">
<p>This is a sample article</p>
<div style="background-color:currentColor">
<p>This is some kind of highlight box.</p>
</div>
</article>
transparent keyword
Note that the CSS Color Module Level 3 spec defines a keyword transparent, which is very useful for overriding previously set colors when required. It is equivalent to rgba(0,0,0,0), which is completely transparent black.
This value used to only be defined as an override value for the background and border property, until it was defined as a true value in CSS3. transparent is supported on all properties in al modern browsers including IE9+.
Opacity property
You can set the opacity of an entire element using the opacity property.
See also
Related articles
Visual Effects
color