Mobile JavaScript best practices
Summary
What to know, what to watch out for to make your apps perform at their best.
When optimising JavaScript, it is important to first understand the big picture and the major stack components affecting performance. Equally important is to understand what can and cannot be optimised in JavaScript without touching the browser codebase. A good starting point for this study is to first take a look at the JavaScript Performance Stack (John Resig’s blog) depicted below.
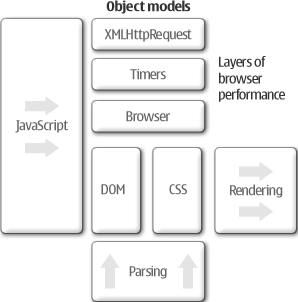
Most importantly:
Pick your battles. First optimise those parts that give you the biggest improvements.
The most performance-intensive operations tend to be reflowing the layout and repainting. When developing with JavaScript, you cannot optimise the browser layout or painting algorithms but you can still affect the performance of these operations by not triggering them unnecessarily.
Here are some common reasons for slow JavaScript performance that can easily be addressed:
- Document Object Model (DOM) Access: Interaction with the DOM is usually slower than normal JavaScript code so should be avoided where possible. For instance, dynamically creating HTML with strings and setting the innerHTML is usually faster than creating HTML with DOM methods.
evalmethod: Whenever possible, avoid theevalmethod as significant overhead is involved in script evaluation.withstatements: Usingwithstatements creates additional scope objects that slow variable access and create ambiguities.for-inloops: Unfortunately, most JavaScript environments have a slow implementation offor-inloops. Opt to traverse arrays instead, using thefor (var i=0; i < array.length; i++)instead of for-in loops.
Note: This material was originally published as part of the Nokia Developer Web Development Library, available as Mobile JavaScript best practices